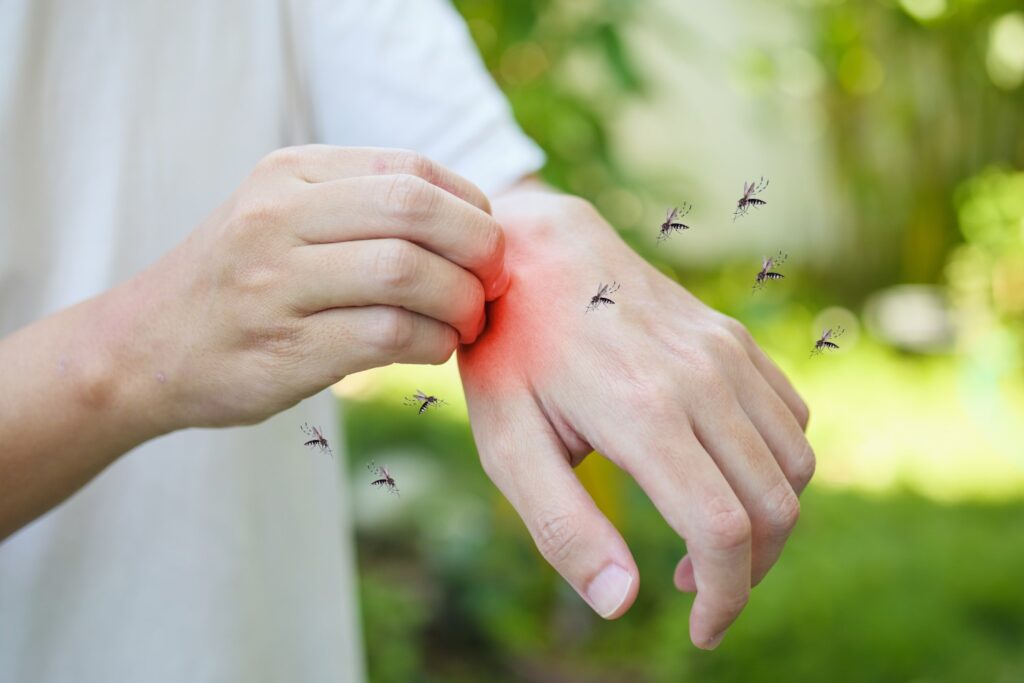
A parasitic infection that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes.
People who have malaria usually feel very sick with high fever and shaking chills.
Symptoms of Malaria
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Nausea
If left untreated, malaria can lead to serious complications such as anemia, kidney failure, and brain damage.
Causes and Risk Factors of Malaria
Malaria is caused by the Plasmodium parasite. The parasites are transmitted to humans through the bite of infected Anopheles mosquitoes.
Risk factors:
- Weakened immune system
- Pregnancy
The risk of malaria is higher for people living or traveling to areas where malaria is prevalent.
Treatment of Malaria
Malaria can be diagnosed through a blood test that can detect the presence of the parasite in the blood.
Treatment includes various medications that depend on the type of malaria and the severity of the infection.
Malaria: Preventive Measures
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and pants
- Sleep under mosquito nets
- Take prophylactic medications while traveling to areas with a high risk of malaria
- Eliminate standing water where mosquitoes can breed
The best way to prevent malaria is to avoid mosquito bites.
Myth and Fact on Malaria
Myth: Taking vitamin B12 can prevent malaria.
Fact: There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that taking vitamin B12 can prevent malaria.
FAQ on Malaria
Can you get malaria from a blood transfusion?
Yes, malaria can be transmitted through blood transfusion. It is important to screen blood donors for malaria to prevent the spread of the infection.
FAQ on Malaria
How long does it take to recover from malaria?
The recovery time for malaria depends on the type and severity of the infection. With appropriate treatment, most people recover from malaria within a few weeks.
Malaria remains a formidable challenge, impacting the lives of millions and hindering socio-economic development in affected regions. However, through continued investment in research, development, prevention, and treatment strategies, progress is being made. It is crucial for governments, organizations, and individuals to sustain their commitment to malaria control, with a focus on strengthening healthcare systems, improving access to prevention measures and treatment, and promoting collaborative efforts. Only through collective action can we hope to achieve a world free from the burden of malaria.