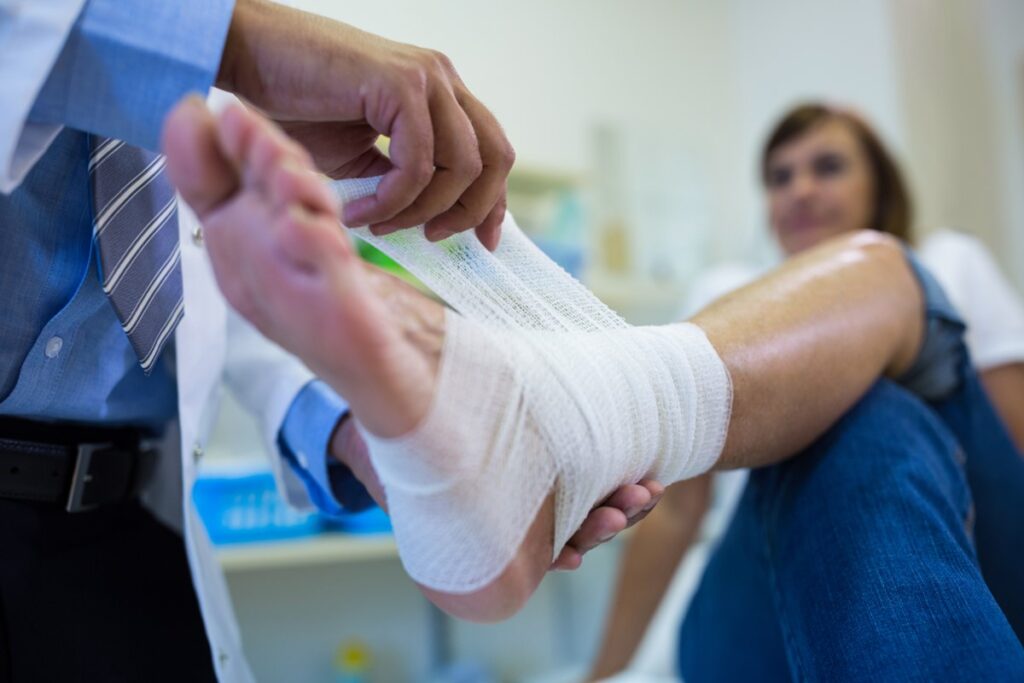
Rehabilitation and recovery play a crucial role in regaining strength, mobility, and function after fracture related infections.
By following a comprehensive rehabilitation program, patients can optimize healing, minimize complications, and restore their quality of life.
Understanding the Healing Process: Fracture related infections can significantly impact the healing process. A comprehensive understanding of the stages of healing, including inflammation, tissue regeneration, and remodeling, helps healthcare professionals tailor the rehabilitation program to each patient’s needs.
Multidisciplinary Approach: Rehabilitation after fracture related infections often requires a multidisciplinary approach. Orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other healthcare professionals collaborate to develop a customized rehabilitation plan that addresses individual needs and goals.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a central role in rehabilitation. It involves exercises and techniques that aim to improve strength, range of motion, flexibility, and functional abilities. Physical therapists guide patients through tailored exercises, gradually progressing towards independence and optimal function.
Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapy focuses on helping individuals regain their ability to perform daily activities, such as dressing, grooming, and cooking. Occupational therapists utilize specialized techniques and adaptive equipment to enhance independence and facilitate a smooth transition back to daily life.
Assistive Devices: Depending on the severity of the fracture related infection and its impact on mobility, assistive devices such as crutches, walkers, or wheelchairs may be necessary during the recovery period. Healthcare professionals provide guidance on the appropriate use of these devices for safe and efficient mobility.
Pain Management: Pain management is a crucial component of rehabilitation. Healthcare professionals employ various strategies, including medications, physical modalities (e.g., heat or cold therapy), and relaxation techniques, to alleviate pain and improve comfort during the recovery process.
Psychological Support: Fracture related infections can take a toll on a patient’s mental well-being. Psychological support through counseling or support groups can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges associated with the recovery process, ensuring a holistic approach to rehabilitation.
Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition is essential for optimal healing and recovery. Healthcare professionals, in collaboration with dietitians, provide nutritional guidance to ensure that patients receive adequate nutrients for tissue repair and overall well-being.
Gradual Return to Activity: As the healing progresses, a gradual return to daily activities, work, and recreational pursuits is encouraged. Healthcare professionals guide patients in safely resuming their previous levels of activity, ensuring that progress is made while minimizing the risk of reinjury.
Long-Term Follow-Up: Long-term follow-up with healthcare professionals is essential to monitor the progress of rehabilitation and address any ongoing concerns or complications. Regular evaluations and adjustments to the rehabilitation plan can optimize outcomes and ensure continued progress.